Tripura at a Glance
Tripura is one of the seven states in the north eastern part of India located between 22 degree and 56 minutes and 24 degree and 32 minutes north latitude and between 90 degree and 09 minutes and 92 degree and 20 minutes east longitude. It is bounded on the north, west, south and south-east by Bangladesh whereas in the east it shares a common boundary with Assam and Mizoram.
The Land: |
|
|---|---|
| Location |
|
| Land |
|
| Climate |
|
The People: |
|
| Population |
|
| Literacy |
|
| Language Spoken |
|
Tripura: The Economy

The economy is primarily agrarian. The primary sector (Agricultural) contributes about 64% of total employment in the state and about 48% of the State Domestic Product (SDP).
The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) growth rate was 10.50% during the 1999-2000 to 2007-2008. The secondary sector share in Gross State Domestic Product has risen from 14.12% to 22.59% during 1999-2000 to 2007-2008.
The per capita income of the State rose from Rs. 14119/- in 1999-2000 to Rs. 28806/- in 2007-08.
A variety of Horticultural/Plantation Crops are produced in Tripura like Pineapple, Oranges, Cashew nut, Jackfruit, Coconut, Tea, Rubber, Other Forest Products and Plantations etc. There is ample scope for increasing the area under such plantations as well as the productivity.
As regards Animal Husbandry and Fisheries, the present level of production is not adequate to meet the demand of the state and there is need and scope for considerable development.
The Industry Sector has also remained too undeveloped so far, despite the vast potential. The secondary sector contributes only about 5% of total employment and about 7% of the total income (SDP) of the state at present.
Tourism has been declared as an Industry in the state since 1987.
Handicraft is emerging as a potential industry in Tripura. The Handloom Industry also plays an important role in rural Industry of Tripura.
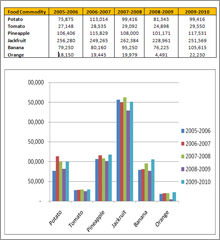
Tripura Agriculture Production Statistics
Agriculture Products:
The major Agricultural Products are as follows.